Custom Alerts
Custom alerts allow you to run a SQL query against the Relevant database at regular intervals to determine whether some condition (or set of conditions) has been met. Once a condition has been met, this will trigger an email to the chosen Relevant users informing them of the alert.
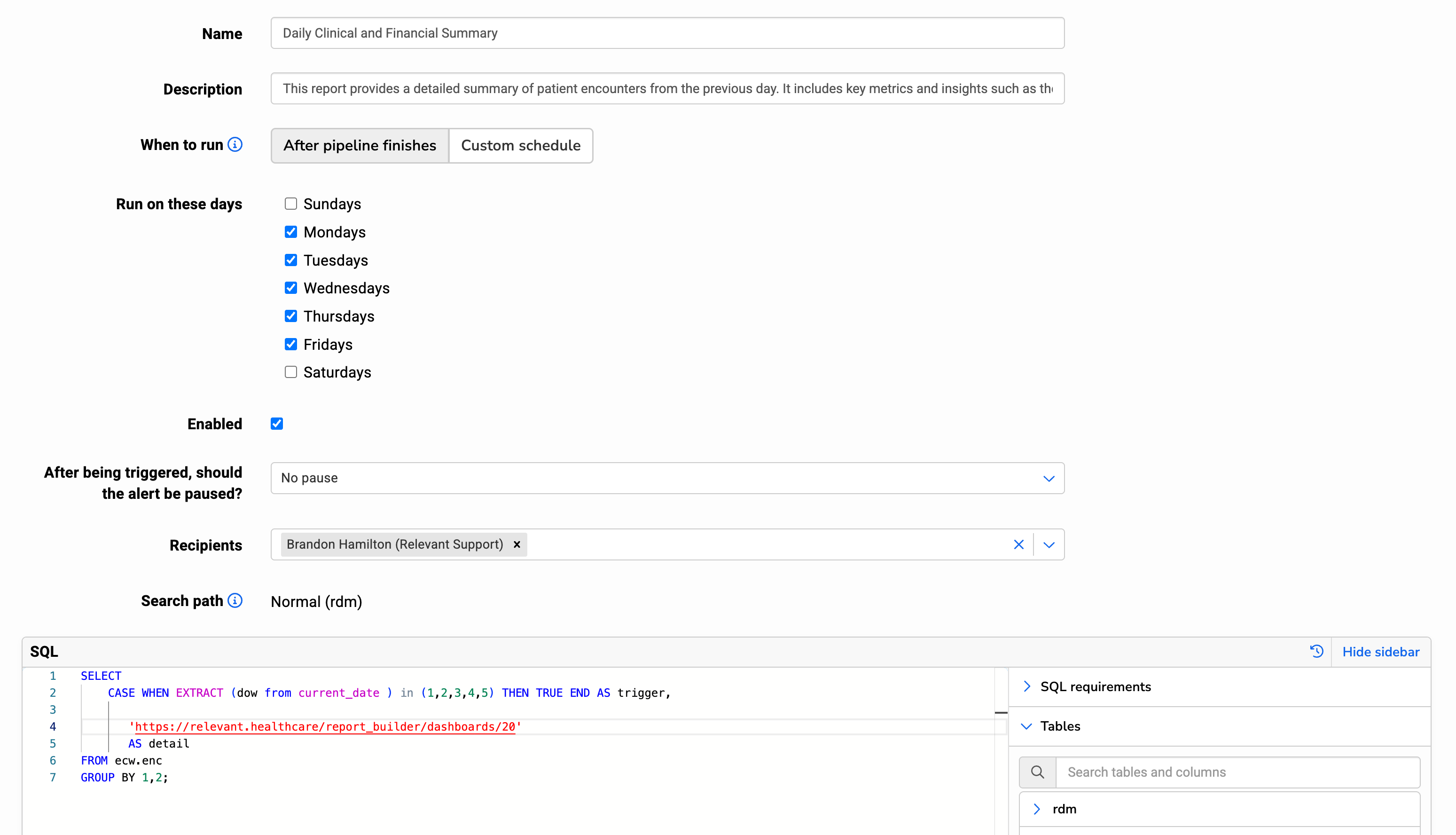
Users with the Manage Data Pipeline ability can set the following settings for custom alerts:
- Name: Labels the Custom Alert and is included in the triggered email
- Description: Is included in the triggered email
- When to run: Alerts can be run as part of the pipeline, or on a cron-based schedule for additional customization.
- Run on these days: If you select “After pipeline finishes”, you can select which days this alert should run after the pipeline. The alert will run as the last step of the pipeline, except if one of these early stages of the pipeline fails: Transformers, Data Elements. See the Data Pipeline Overview article for more details.
- Schedule: A standard, five-field cron expression that determines when/how often to run the alert SQL to check for a trigger. All times are in New York/Eastern Time. Cron expressions are very flexible and many online tools can help generate cron statements, such as crontab guru.
- After being triggered, should the alert be paused?: This allows you to pause or snooze the alert for a period of time after the alert is triggered, so that you don’t continue to receive email notifications before you can correct or re-set the alert.
- Recipients: Users who will be emailed alert notifications if the alert is triggered. Alerts must have at least one user configured at all times. If an alert has a single user configured and that user is removed from Relevant, the alert will be automatically disabled.
- Search path: Database schema from which the SQL will select tables.
- SQL: The query that defines the conditions for which an alert triggers. The final select statement SQL accepts the following columns:
trigger: a boolean, or TRUE/FALSE, value. When the alert query runs and the value oftriggeris TRUE, the alert triggers, sends an email to selected recipients, and pauses future runs of the alert query for the period of time selected.detail: a text value. This can contain any text, whether static or dynamic based on data. The detail will NOT be included in the alert email, but is accessed from Relevant through a link provided in the alert email. Therefore, it can securely contain PHI.- While the alert SQL’s final SELECT statement can only contain the above two columns, alert SQL may contain temporary tables and functions.
